DUNNAGE BAGS
Dunnage bags are mainly used in containers, ships, railway wagons and in some special cases in trailers.
Dunnage bags are a fast and efficient method of securing, in general, uniform loads such as pallets, carton packaging, cases and crates . They replace costly and time consuming wooden construction otherwise necessary.
Easygu dunnage bags consist of a Polyethylene inner-liner and 1, 2 or 4 layers of wet-strength paper. The total strength of a dunnage bags is dependant on the quality of paper, the number of layers used and the way they are glued together. The construction of the Easygu dunnage bag valve allows it to be used both for one-way applications and also for applications where a reusable bag is more economical.
Typical dunnage bag applications:
Type | Load Carriers | Goods |
CDB 1-ply | Container / truck | E.g. furniture |
CDB 2-ply | Container / truck | Pallets / cases / crates |
CDB 4-ply | Container / truck | Pallets / coils of paper |
Intermodal | Container / truck | Pallets / cases / crate |

CALCULATIONS
To ensure that a load will arrive at it's destination safely and in the same condition as it left the loading point, a calculation has to be made as to the amount of load securing material required.
Consideration has to be taken of a number of factors such as the weight of the load and the forces which will come to bare on the load during transport.
The I.M.O. publication "1994/1995 Amendments to the Code of Safe Practice for Cargo Stowage and Securing" allows for 2 possible methods to be used:
A) Rule-of-thumb method (simple method for general use)
B) Advanced Calculation Method (for specific calculations where all factors can be taken into consideration).
Based on the fact that most loading crews do not have access to all relevant information as to position of a container on board ship, expected wind and sea slosh forces underway, acceleration factors etc., Easygu base their calculation on the simple rule-of-thumb method.
Should all relevant factors be available, we shall be glad to calculate according to the Advanced Calculation Method.
Rule-of-thumb method
Assumptions: a) a transverse acceleration of 1g
b) transverse lashing angles
c) adequate use of friction increasing materials (e.g. anti-slip mats)
I.M.O. Rule: "The total of the MSL values of the securing devices on each side of a unit cargo (port as well as starboard) should equal the weight of the unit."
Formulae: MSL per side = load weight (kN)
Before an example calculation can be made a number of relevant terms have to be further considered.
MSL (Maximum Securing Load)
MSL (Maximum Securing Load) is a term used to define the load capacity for a device used to secure cargo to a ship. MSL is to securing devices as "Safe Working Load" is to lifting tackle.
| Typical MSL Values | Material | MSL |
Shackles, rings etc. | 50% |
Fiber rope | 30% |
Web lashin | 50% = Cordlash |
Wire rope (single use) | 80% |
reuse | 30% |
Steel band (single use) | 70% |
Chains | 50% |
System strength
One-way lashings are seldom used in a single strand but mostly as a "system" i.e. in a loop between load and load carrier with a heavy duty buckle in between as joint.

The total strength of this system is termed "system strength" and the value is dependant on a number of factors i.e. the type of buckle used and the nature of the loop construction over the load.
Below you will find a chart of cordlash systems and their MSL values.
Load securing methods
There are two basic load securing methods; direct lashing and tying down.
Direct Lashing
With direct lashing, lashings are attached directly to the unit load in the direction of movement i.e. forwards, backwards and side wards. Due to the vertical lashing angle there is also an element pulling the load downwards directly on to the load carrier.
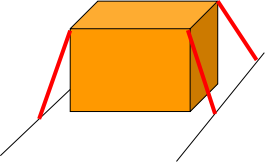
As part lashings can not be made, we always go to the next full lashing, in this case 3 lashings per side.
In 6.1. above, the I.M.O. points out that adequate friction should be provided by using suitable materials.
Easygu advises the use of rubber anti-slip mats for securing unit-loads. This increases the friction for most load/carrier combinations by a factor 3 and adds to the total safety.
Tying down
When tying down, the lashing is placed over the load either as a single lashing secured on both sides to the load carrier or double with one or two buckles as joint.
With this method, the force restraining movement of the unit load is provided by the additional friction created by tension brought into the lashing.
It is therefore important to a) bring in as much tension as possible to the lashing (not exceeding 50% of the lashing strength, linear or system)
b) use anti-slip mats to increase the frictional forces to a maximum.
Using two buckles (one per side) will give the maximum of tension in all parts of the lashing.
Easygu has the ideal tooling for this method of securing where the maximum of tension can be applied either manually or pneumatically.




















